This may work for a larger dataset: create a list of all the Key values you need from the dfRight Dataset in the example. Rename the Column1Right and Column2Right column headers (Keys) to become the same as in dfLeft. Join the selection and its inverse selection from the two datasets.
selection = {"A", "B"};
Join[Select[MemberQ[selection, #Key] &]@
Query[All,
KeyMap[Replace[{"Column1Right" -> "Column1",
"Column2Right" -> "Column2"}]]]@dfRight,
Select[! MemberQ[selection, #Key] &]@dfLeft]
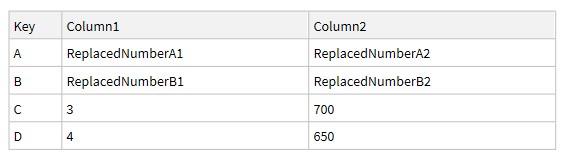
This approach works, because the two Datasets have the same number of columns and the Key values are distinct. I suspect your Python code works for the same reason as well (I haven't tried for Dataframes with dissimilar number of columns in Pandas).
In a more generic case e.g. when the Datasets dfRight and dfLeft do not have the same number of columns and the Key values are still distinct, you can use:
replacement[x_] := {{Part[#, 1, 1] &@Position[x]@dfLeft, "Column1"} ->
Query[Part[#, 1, 1] &@Position[x]@dfRight, "Column1Right"]@
dfRight, {Part[#, 1, 1] &@Position[x]@dfLeft, "Column2"} ->
Query[Part[#, 1, 1] &@Position[x]@dfRight, "Column2Right"]@dfRight}
ReplacePart[Flatten[replacement /@ selection, 1]]@dfLeft
The last approach will replace the Column1 and Column2 values for each selected key in dfLeft by its Column1Right and Column2Right values from dfRight. All you have to do now is provide a complete "selection" list.