Wolfram notebook is attached at the end of the post.
This post is about FEM simulation of violin vibration modes in 3D. As well known there are Helmholtz resonances of air inside the violin body with frequencies dependent on geometry of f-holes. This is the main reason why violin has so pronounced sound. To simulate these modes with Mathematica FEM we first define the body geometry (this is my design with given volume and area of f-holes, but it taken from the real violin):
xy = {{3.805405405405406`,3.34954954954955`},{3.8252252252252257`,6.6990990990991`},{3.9441441441441443`,7.9081081081081095`},
{4.47927927927928`,8.601801801801802`},{5.014414414414414`,8.264864864864865`},{4.816216216216216`,7.8882882882882885`},
{4.895495495495496`,7.630630630630631`},{5.232432432432433`,7.432432432432433`},{5.47027027027027`,7.491891891891892`},
{5.648648648648649`,7.8882882882882885`},{5.668468468468468`,8.046846846846847`},{5.56936936936937`,8.403603603603605`},
{5.252252252252252`,8.681081081081082`},{4.855855855855856`,8.780180180180182`},{4.518918918918919`,8.8`},
{3.9639639639639643`,8.522522522522523`},{3.567567567567568`,7.967567567567568`},{3.3693693693693696`,7.372972972972973`},
{3.2306306306306305`,6.67927927927928`},{3.1513513513513516`,3.3693693693693696`},{3.1513513513513516`,2.655855855855856`},
{2.9729729729729732`,1.783783783783784`},{2.8738738738738743`,1.4666666666666668`},{2.100900900900901`,0.7927927927927928`},
{1.7243243243243245`,1.3081081081081083`},{2.021621621621622`,1.7639639639639642`},{2.0414414414414415`,2.0414414414414415`},
{1.9621621621621623`,2.23963963963964`},{1.6648648648648652`,2.4378378378378383`},{1.4666666666666668`,2.5171171171171176`},
{1.10990990990991`,2.338738738738739`},{0.891891891891892`,1.9423423423423425`},{0.9315315315315316`,1.4072072072072073`},
{1.5657657657657658`,0.7927927927927928`},{2.081081081081081`,0.6342342342342343`},{2.5963963963963965`,0.7927927927927928`},
{3.0918918918918923`,1.2090090090090093`},{3.5081081081081082`,1.902702702702703`},{3.706306306306306`,2.6954954954954955`}};
reg1 = RegionUnion[Disk[{0, 19.5/2}, 19.5/2],
Disk[{0, 36 - 15.5/2}, 15.5/2],
Rectangle[{-10, 15}, {10, 25}]]; reg2 =
RegionDifference[reg1,
RegionUnion[Disk[{-10, 20}, 9.5/2], Disk[{10, 20}, 9.5/2]]];
c0 = {0, 36 - 15.5/2}; c1 = {7.03562, 25};
f[x_] := c0[[2]] + x (c1[[2]] - c0[[2]])/(c1[[1]] - c0[[1]]); r1 =
Norm[c1 - {10, f[10]}];
reg3 = RegionDifference[reg2, Disk[{10, f[10]}, r1]];
f1[x_] := c0[[2]] - x (c1[[2]] - c0[[2]])/(c1[[1]] - c0[[1]]);
reg4 = RegionDifference[reg3, Disk[{-10, f1[-10]}, r1]]; c10 = {0,
19.5/2}; c11 = {8.215838362577491`, 15};
f11[x_] := c10[[2]] + x (c11[[2]] - c10[[2]])/(c11[[1]] - c10[[1]]);
r2 = Norm[c11 - {10, f11[10]}];
reg5 = RegionDifference[reg4, Disk[{10, f11[10]}, r2]];
f12[x_] := c10[[2]] - x (c11[[2]] - c10[[2]])/(c11[[1]] - c10[[1]]);
reg6 = RegionDifference[reg5, Disk[{-10, f12[-10]}, r2]]; p6 =
RegionPlot[reg6, AspectRatio -> Automatic];
fh[xf_, yf_] :=
RegionUnion[
Polygon[Table[{xy[[i, 1]] - xf, xy[[i, 2]] + yf}, {i,
Length[xy]}]],
Polygon[Table[{-xy[[i, 1]] + xf, xy[[i, 2]] + yf}, {i,
Length[xy]}]]];
General view of the violin body from the front and back side
Show[p6, Graphics[fh[7, 12], AspectRatio -> Automatic]]
dz = 3.79; reg8 =
ImplicitRegion[Element[{x, y}, reg6] && 0 <= z <= dz, {x, y, z}];
mesh3d1 = DiscretizeRegion[reg8, {{-10, 10}, {0, 36}, {0, dz}}]
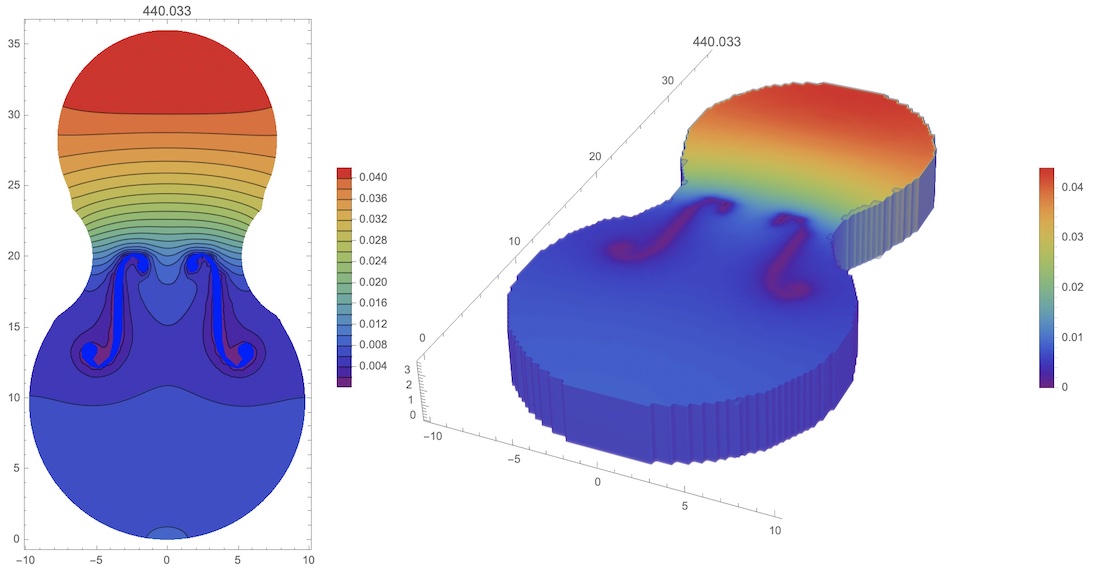
Next step is the computation of air modes in the violin body with using NDEigensystem[] as follows
ca = 34321(*T=20C*); L = -Laplacian[u[x, y, z], {x, y, z}]; {vals, funs} =
NDEigensystem[{L,
DirichletCondition[u[x, y, z] == 0,
Element[{x, y}, fh[7, 11.49]] && z == dz]}, u,
Element[{x, y, z}, mesh3d1], 15];
Finally we visualize first 5 modes and the main mode in 3D
{Table[DensityPlot[funs[[i]][x, y, dz/2], {x, -10, 10}, {y, 0, 36},
PlotRange -> All, PlotLabel -> ca Sqrt[vals[[i]]]/(2 Pi),
ColorFunction -> "Rainbow", AspectRatio -> Automatic], {i, 1,
5}],
DensityPlot3D[
funs[[1]][x, y, z], {x, -10, 10}, {y, 0, 36}, {z, 0, dz},
PlotRange -> All, PlotLabel -> ca Sqrt[vals[[1]]]/(2 Pi),
ColorFunction -> "Rainbow", AspectRatio -> Automatic,
PlotLegends -> Automatic, PlotPoints -> 100, BoxRatios -> Automatic,
OpacityFunction -> None, Boxed -> False]}
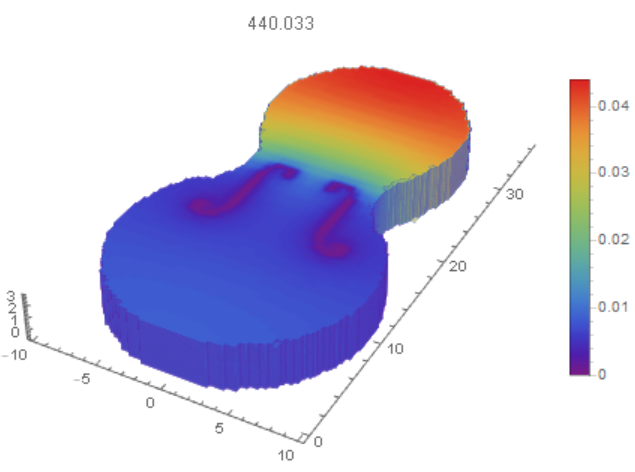 Therefore the first mode of 440.033 Hz is close to "A4" (440 Hz) tone. But we expecting "C4" (261.626 Hz), or "C#4" (277.183 Hz). The main reason of this discrepancies could be the wood plate vibration from the back side. Thus we define mesh, parameters of the wood plate and modes as follows
Therefore the first mode of 440.033 Hz is close to "A4" (440 Hz) tone. But we expecting "C4" (261.626 Hz), or "C#4" (277.183 Hz). The main reason of this discrepancies could be the wood plate vibration from the back side. Thus we define mesh, parameters of the wood plate and modes as follows
dreg = DiscretizeRegion[reg6, {{-10, 10}, {0, 36}},
MaxCellMeasure -> .05]
Y = 10.8*10^9; nu = 31/100; rho = 500; h = .003; d =
10^4 Sqrt[Y h^2/(12 rho (1 - nu^2))];Ld2 = {Laplacian[-d u[x, y], {x, y}] +
v[x, y], -d Laplacian[v[x, y], {x, y}]};
{vals, funs} =
NDEigensystem[{Ld2, DirichletCondition[u[x, y] == 0, True]}, {u, v},
Element[{x, y}, dreg], 5];
Table[DensityPlot[Re[funs[[i, 1]][x, y]], {x, y} \[Element] dreg,
PlotRange -> All, PlotLabel -> vals[[i]]/(2 Pi),
ColorFunction -> "Rainbow", AspectRatio -> Automatic], {i, 2,
Length[vals]}]
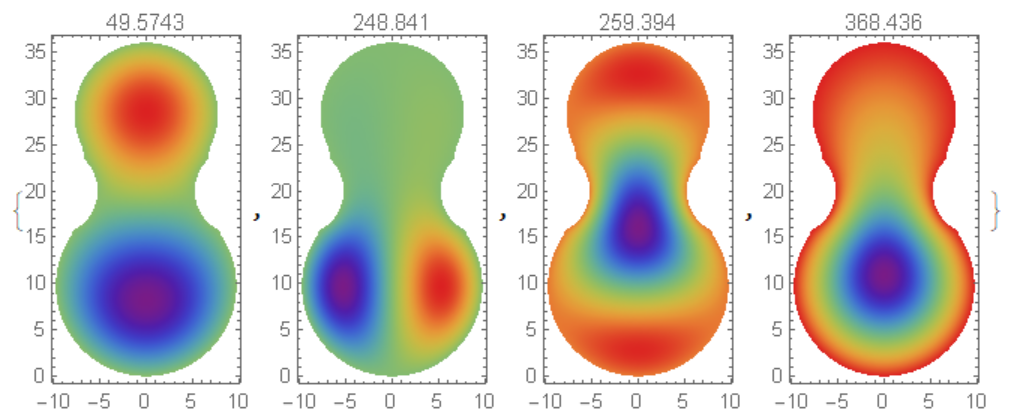 Hence for wood plate we have mode of 259.394 Hz and it is close to C4 tone.
Hence for wood plate we have mode of 259.394 Hz and it is close to C4 tone.
 Attachments:
Attachments: