Hi Dan,
I do not have any experience in astrophotography and I hope my little remark is not completely off topic: As far as I understand your question, it is about judging sharpness of an image. Here fouriertransform might be an option: The sharper an image, the more spread out are the corresponding fourier values, which can be calculated in terms of standard deviation. This should be an easy, fast and robust method - to be used not just for star images. So I wrote a little function (should be self explaining):
imageSharpness[img_Image] :=
Module[{imgData, fouData, qRows, qColumns, qData0, qData1},
imgData = ImageData[ColorConvert[img, "Grayscale"]];
(* dimensions of one quarter: *)
fouData = Abs@Fourier[imgData];
{qRows, qColumns} = Dimensions[fouData]/2;
(* get the data of the first quarter: *)
qData0 = fouData[[;; qRows, ;; qColumns]];
(* get indizes, remove first line and first column and flatten: *)
qData1 = Flatten[MapIndexed[{#2, #1} &, qData0, {2}][[2 ;;, 2 ;;]], 1];
(* return something like "standard deviation": *)
Mean[(#1[[1]]^2 + #1[[2]]^2) #2 & @@@ qData1]
]
Lets try it out:
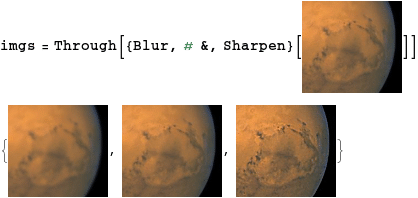
then
imageSharpness /@ imgs
(* Out: {6.2140,11.9367,25.72055} *)
Maybe this might somehow helpful.
Henrik