Update 2 - EARTH’S MOST COMPLEX MINERAL:
- Ewingite: Earth’s most complex mineral
Ewingite is the most complex mineral on Earth, so I thought it would be interesting to use the CrystalLattice function to reproduce it’s visualization.
But there is still no Ewingite .CIF file available. So to make it possible, I manually edited and developed a .CIF file with the Ewingite information (this .CIF is attached for those interested). The information on this mineral was extracted from few articles (the links are at the end of this Update 2 and in the attach).
Image 1 (basic information - see link 1):

Image 2 (place of discovery - see link 1):
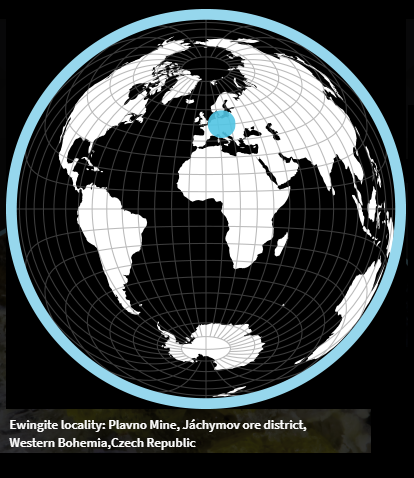
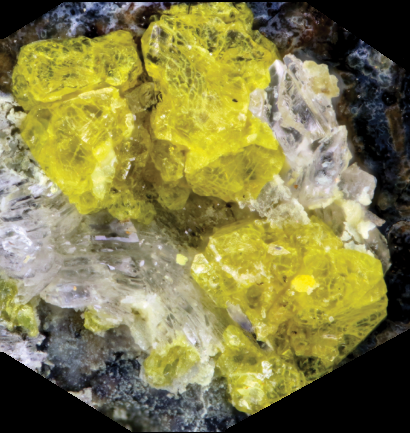
Image 3 (real image of the mineral - golden yellow):

- Codes (.CIF + using CrystalLattice function):
First, what the .CIF of the mineral Ewingite looks like without taking into account the mineral's natural water molecules (NW – No Water):
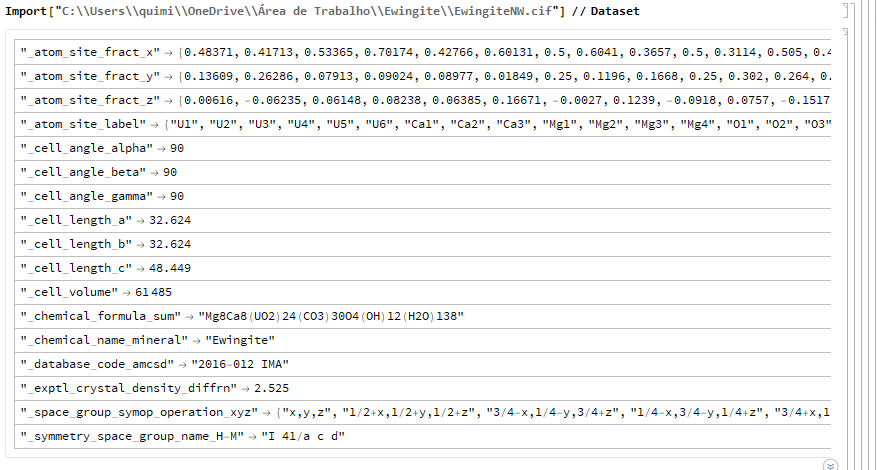
ewNW = CrystalLattice[
"C:\\Users\\quimi\\OneDrive\\Área de \
Trabalho\\Ewingite\\EwengiteNW.cif"]

After creating Ewingite's CrystalLattice object, we apply CrystalLatticeModify to perform spatial symmetry in a unit cell:
ewNWsym = CrystalLatticeModify[ewNW, {"UnitCellCopy", {0, 0, 0}}]

After that, we check the density of the object with the density of the X-ray crystallography (note that the value is very close to that of the article):
valueD = CrystalLatticeValue[ewNWsym,
"CellDensity"]; UnitConvert[valueD, {"Grams"/"Centimeters"^3}]

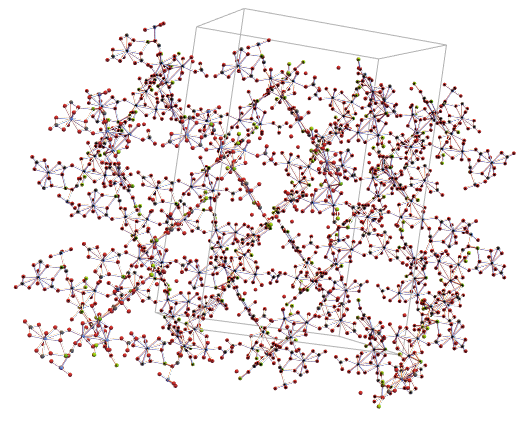
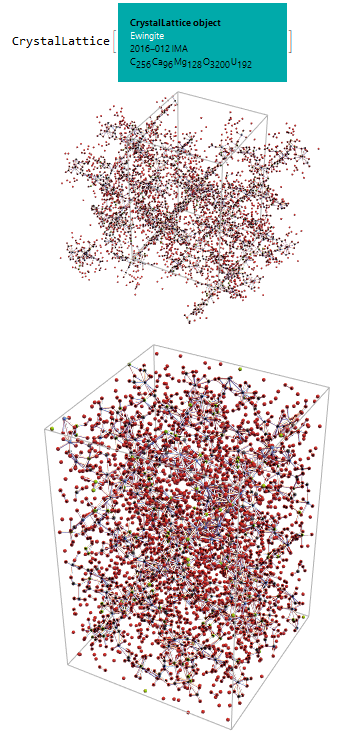
So, we generated the 3D graph using CrystalLatticePlot3D, note that even without the water molecules this seems to be a very complex mineral:
CrystalLatticePlot3D[ewNWsym]
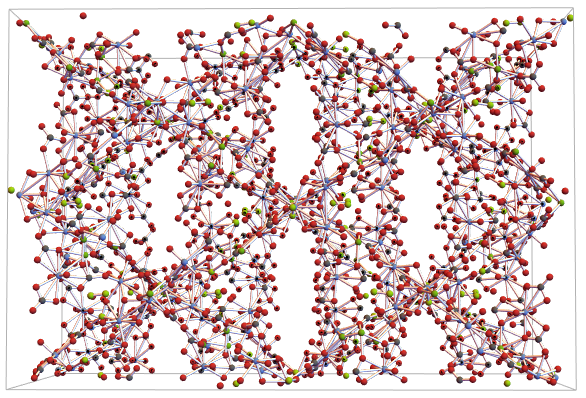
Refining the visualization using the CrystalLatticeModify function in conjunction with the “UnitCellGather” argument. We can better see its structure inside the unit cell:
ewNWsymGather =
CrystalLatticeModify[ewNWsym,
"UnitCellGather"]; CrystalLatticePlot3D[ewNWsymGather]
Now, comparing with the symmetry given in the article (we can see that the information proceeds):
Image 4 (Space Group symmetry - in attachment 1):
Finally, to have a glimpse of the real complexity, the coordinates of the oxygen atoms from the water molecules found in the mineral Ewingite were inserted in the .CIF file. Even so, the visualization still lacks the +3500 hydrogen atoms of this water that was not added due to difficulties in the data information:
ew = CrystalLattice[
"C:\\Users\\quimi\\OneDrive\\Área de \
Trabalho\\Ewingite\\Ewingite.cif"]; ewSym =
CrystalLatticeModify[ew, {"UnitCellCopy", {0, 0, 0}}]; plot1 =
CrystalLatticePlot3D[ewSym]; ewSymGather =
CrystalLatticeModify[ewSym, "UnitCellGather"]; plot2 =
CrystalLatticePlot3D[ewSymGather]; {ewSym, plot1, plot2} // Column
Ewingite: Earth’s most complex mineral Travis A. Olds1 , Jakub Plasil2 , Anthony R. Kampf3 , Antonio Simonetti1 , Luke R. Sadergaski1 , Yu-Sheng Chen4 and Peter C. Burns1,5: file in attach*.
https://zh.mindat.org/min-47791.html (images 1 and 2)
Thank you.
 Attachments:
Attachments: