NOTE: see the article below about making this website or click on the image to go to the actual website.
Because WL has immense and constantly increasing vocabulary of functions and data (THE only language that has an ocean of built-in curated data), it is easy to come up with fun challenges or pack whole applications in a few lines of code. Below there are 3 examples that compute person's age on other planets in planet's days and years. Starting with very simple code-golfing exercises it is quite fast to build up to a whole beautiful interactive website and I will walk you through this.
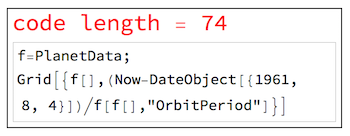
Code Golf: 74 characters
Code golf is a fun coding competition with participants aiming for the shortest possible code that implements an algorithm.
Can anyone come up with a shorter version version of the following code?
f=PlanetData;Grid[{f[],(Now-DateObject[{1961, 8, 4}])/f[f[],"OrbitPeriod"]}]
or prettified version:
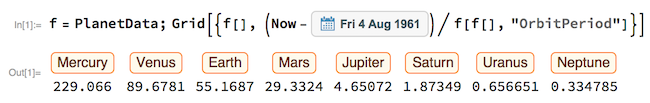
Here the date is assumed to be someone's birthday (for the curious - who's birthday is it?). The output should be in a nice readable table-like from. According to this little counter I got 74 characters:
Framed[Column[{
Dynamic[Style["code length = "<>ToString[StringLength[StringDelete[x," "]]],20,Red]],
InputField[Dynamic[x],String,ContinuousAction->True,FieldHint->"Enter code in InputForm"]
}]]
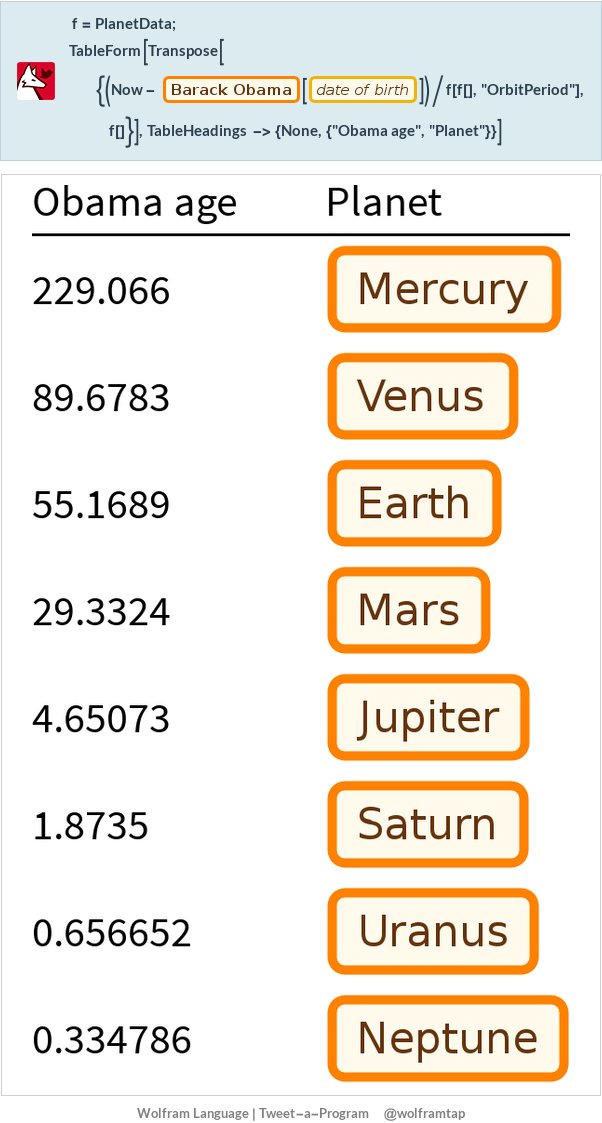
Tweet-a-Program
Another challenge actually would be to make a nice tweet out of it for Wolfram Tweet-a-Program (TaP). Interesting thing is not to use just a date, but a famous person name. Can you make this shorter? Code for Tap (note the syntax =[...] as it is the equivalent of CTRL+= in front end) and the actual tweet itself:
f=PlanetData;TableForm[Transpose[{(Now- =[Obama bday])/f[f[],"OrbitPeriod"],f[]}],TableHeadings->{None,{"Obama age","Planet"}}]
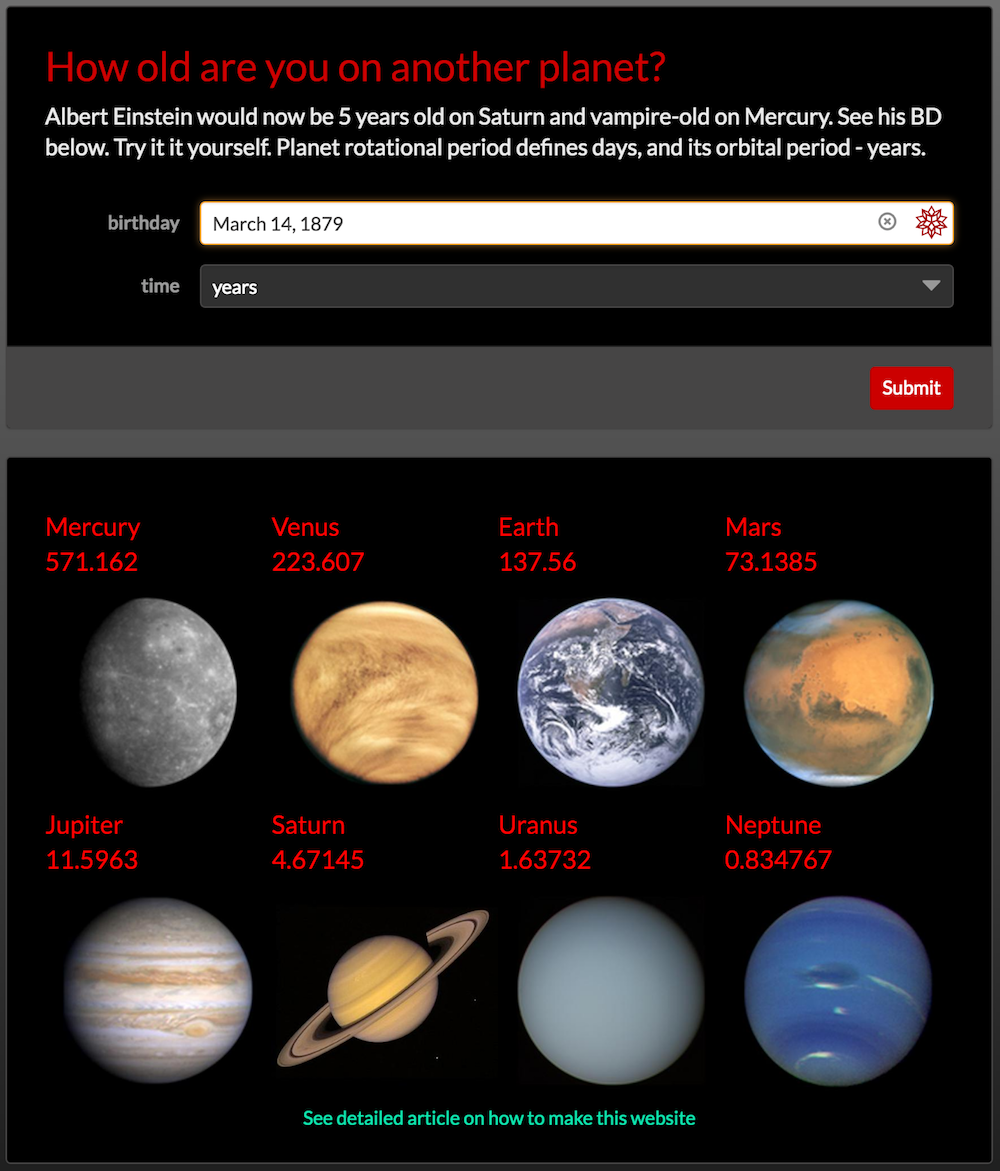
Interactive microsite
It is important to remember that due to planet's "OrbitPeriod" property we are considering age in years. We could consider planet's "RotationPeriod" around axis and so count the age in planet's days. Code will still stay so short that it is easy to build a whole microsite from it giving people interface to play with their birthday dates and astronomy facts. Here is a simple function that gets astronomical data and oranges them into a table.
hoap[bd_,u_]:=Module[
{period,imgs,
data=EntityValue["Planet", {"Name","Image","RotationPeriod","OrbitPeriod"}]},
period=(Now-bd)/data[[All,u]];
imgs=ConformImages[data[[All,2]],400];
Style[
Grid[{
data[[;;4,1]],period[[;;4]],imgs[[;;4]],
data[[-4;;,1]],period[[-4;;]],imgs[[-4;;]]},
Alignment->Left],
FontSize->20,Red]
]
To design user interface via a microsite we will use FormPage function:
CloudDeploy[
FormPage[
{"birthday"->"Date",
"time" -> {"years" -> 4, "days" -> 3}},
hoap[#birthday,#time]&,
AppearanceRules-><|
"Title" -> "How old are you on another planet?",
"Description" -> "
Albert Einstein would now be 5 years old on Saturn and vampire-old on Mercury. See his BD below. Try it it yourself.
Planet rotational period defines days, and its orbital period - years."|>,
FormTheme -> "Black"
][<|"birthday" -> "March 14, 1879", "time" -> 4|>],
"howoldplanet",Permissions->"Public"]
Out[]= CloudObject["https://www.wolframcloud.com/objects/user-3c5d3268-040e-45d5-8ac1-25476e7870da/howoldplanet"]
It gives us a URL if a cloud object where our microsite resides. To have a shorter version we compute:
URLShorten[%[[1]], "howoldplanet"]
https://wolfr.am/howoldplanet
and following that URL you will arrive at a simple but stylish microsite shown at the top of this page. Hooray!